Pubic Symphysis Force
Overview
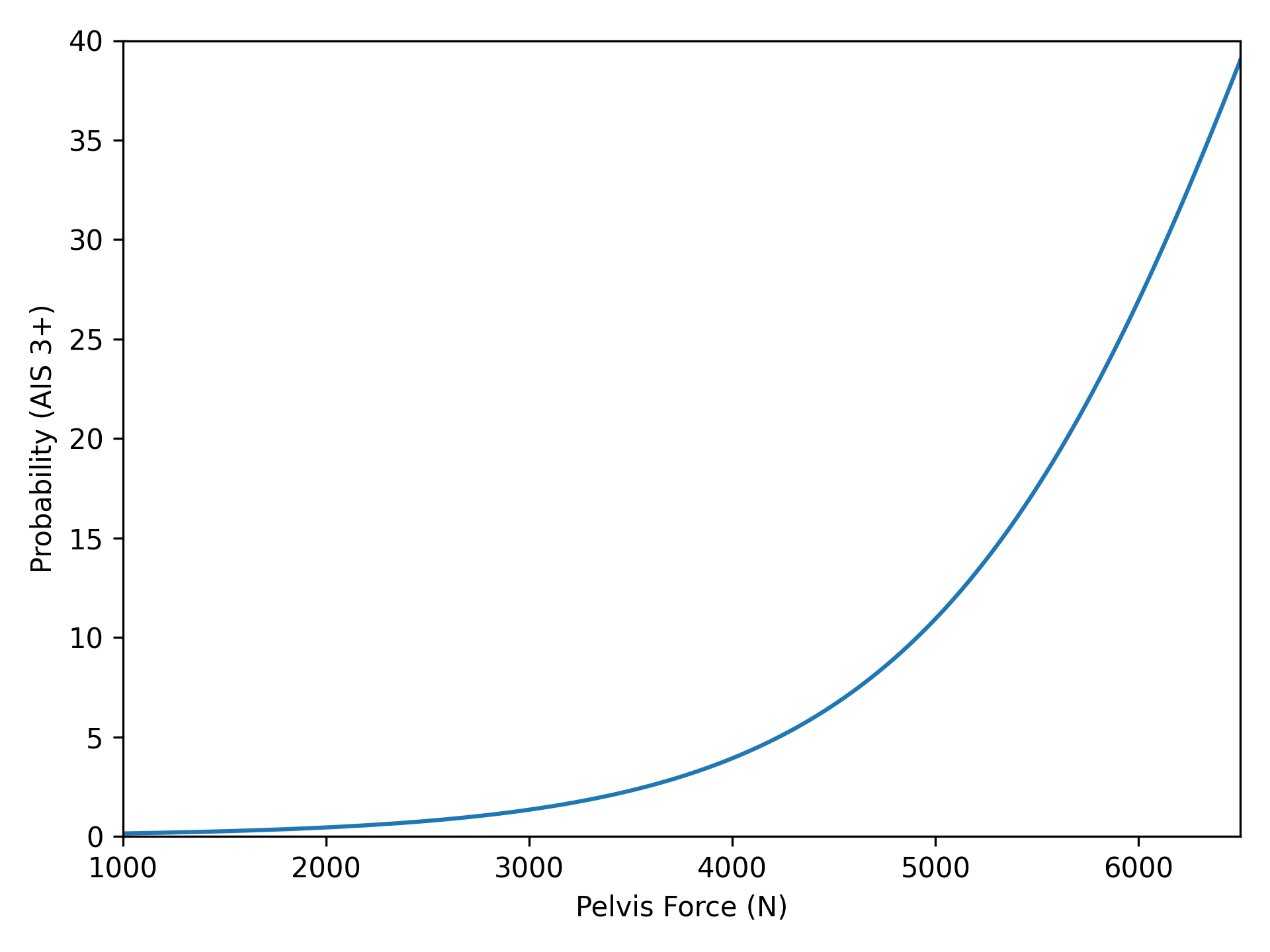
Lateral force measured at the pubic symphysis refers to the forces acting on either side of the pubic symphysis during a car crash [1]. High levels of laterally applied force to the pubic symphysis can result in pelvic fractures, internal bleeding, or lumbar spine damage [2]. Additionally, if an Injury Assessment Reference Value (IARV) is associated with the ATD used in the selected load test, the calculated maximum lateral force will be reported as a percentage of the IARV [3]. The IARV represents a threshold value used to assess the risk of injury during an impact. Each ATD has its own IARV, which varies depending on the type, sex, and size of the dummy [3].
Required Signals
- Force at the Pubic Symphysis (Y)
Calculation
- Convert the pubic symphysis force to newtons (N) (if applicable)
- Filter the pubic symphysis force (CFC = 600)
- Signal is truncated to start at 0 seconds (if applicable)
- Finds the maximum absolute filtered force
- Calculates the percent of the IARV threshold that the calculated maximum absolute pubic symphysis force reaches
Pubic Symphysis Force IARV Table [4]
| ATD | IARV (N) |
|---|---|
| EuroSID | 6000 |
NCAP Combined Injury Rating
The pelvis force metric for ES-2re is used for the NCAP side MDB and side pole tests.
References
[1] Leport, T., Baudrit, P., Trosseille, X., Petit, P., Palisson, A., & Vallancien, G. (2007). Assessment of the pubic force as a pelvic injury criterion in side impact. SAE Technical Paper 2007-22-0019.
[2] Tile, M., Helfet, D., & Kellam, J. (2003). Fractures of the Pelvis and Acetabulum.
[3] "Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation". Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures, Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, June 2009.
[4] Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 49 CFR § 571.214; Side impact protection.
[5] National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Final Rule; Response to Petitions for Reconsideration: Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards; Head Restraints. Docket No. NHTSA-2006-26555-0120, U.S. Department of Transportation, 2006.