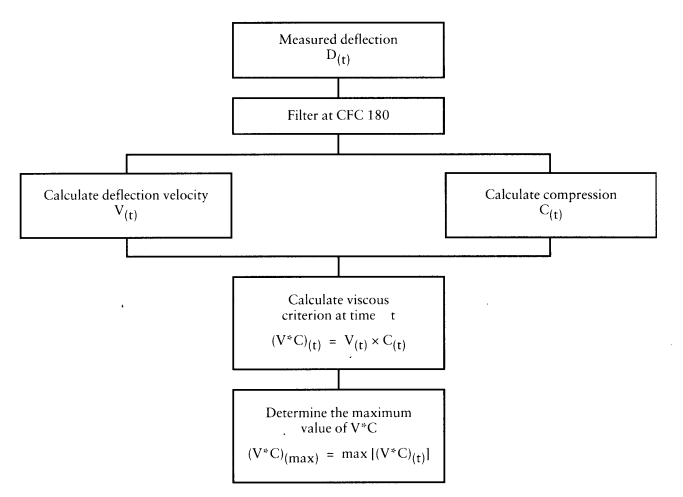
Viscous Criterion (VC)
- SAE Method 1
- SAE Method 2
- Directive 96/27/EC
- SID 2S Method
Overview
The first method in SAE 1727 uses thorax deflection to understand the compression of the chest during frontal or side impacts. This injury criatria is used to predict soft tissue injuries in the soft tissues of the thorax.
Inputs
Signals
- Thorax Deflection (Sternum Deflection, Chest Deflection, or Rib Deflection for Frontal (X) or Side (Y) Impacts)
Calculation
- Filter the thorax deflection data according to SAE J211-1 (CFC = 600)
- Differentiate deflection using equidistant differentiation method
- Calculate Viscous Criteria vs Time
- Take the maximum of the Viscous Criteria vs Time
The viscous criteria scale factor and chest depth noprmalization from SAE 1727 [1]
| ATD | Viscous Criteria Scale Factor | Chest Depth Normalization (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| HIII - M95 | 1.3 | 254 |
| HIII - M50 | 1.3 | 229 |
| HIII - F05 | 1.3 | 187 |
| HIII - 6yo | 1.3 | 143 |
| HIII - 3yo | 1.3 | 122 |
| SID-IIs | 1.0 | 138 |
| EuroSID | 1.0 | 140 |
Viano and Lau graph of viscous criterion to understand the impacts of chest compression and rate of chest compression in terms of soft issues injury [2].
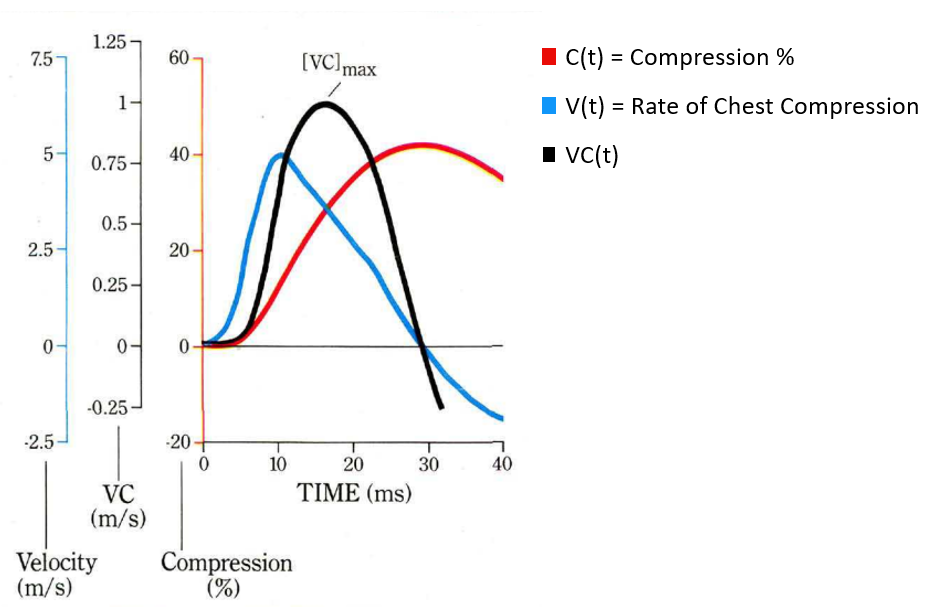
Injury Criteria
Injury criteria for chest from IIHS [3],
| Parameter | IARV | Good - Acceptable | Acceeptable - Marginal | Marginal - Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternum Deflection (mm) | -50 | -50 | -60 | -75 |
| Sternum Deflection Rate (m/s) | -8.2 | -6.6 | -8.2 | -9.8 |
| Viscous Criterion (m/s) | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
References
[1] "Calculation Guideline for Impact Testing" No. J1727-2015-02 SAE International. SAE Technical Report, 2015.
[2] Lau, Ian V., and David C. Viano. "The viscous criterion - bases and applications of an injury severity index for soft tissues." SAE transactions (1986): 672-691.
[3] "Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation - Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures" No. 2009-06. Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), 2009.
Overview
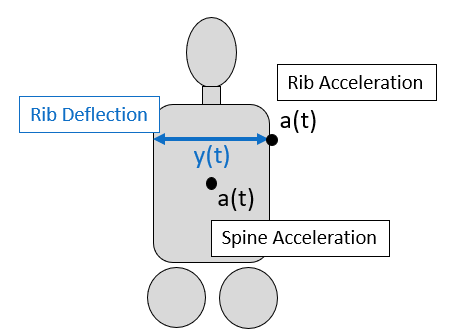
The second method in SAE 1727 uses rib deflection, rib acceleration, and spine accelerations to understand chest compression and rate of compression for the thorax. This injury criatria is used to predict soft tissue injuries in the soft tissues of the thorax.
Inputs
Signals
- Rib Deflection (Y)
- Rib Acceleration (Y)
- Spine Acceleration (Y)
Calculation
- Filter the rib deflection data according to SAE J211-1 (CFC = 600)
- Filter Rib Acceleration and Spine Acceleration (CFC = 600)
- Integrate Rib Acceleration and Spine Acceleration
- Convert to m/s
- Calculate the rate of compression by taking the difference in the velocities
- Calculate Viscous Criteria vs Time
- Take the maximum of the Viscous Criteria vs Time
The viscous criteria scale factor and chest depth noprmalization from SAE 1727 [1]
| ATD | Viscous Criteria Scale Factor | Chest Depth Normalization (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| HIII - M95 | 1.3 | 254 |
| HIII - M50 | 1.3 | 229 |
| HIII - F05 | 1.3 | 187 |
| HIII - 6yo | 1.3 | 143 |
| HIII - 3yo | 1.3 | 122 |
| SID-IIs | 1.0 | 138 |
| EuroSID | 1.0 | 140 |
Injury Criteria
Injury criteria for chest from IIHS [3],
| Parameter | IARV | Good - Acceptable | Acceeptable - Marginal | Marginal - Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternum Deflection (mm) | -50 | -50 | -60 | -75 |
| Sternum Deflection Rate (m/s) | -8.2 | -6.6 | -8.2 | -9.8 |
| Viscous Criterion (m/s) | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
References
[1] "Calculation Guideline for Impact Testing" No. J1727-2015-02 SAE International. SAE Technical Report, 2015.
[2] Lau, Ian V., and David C. Viano. "The viscous criterion - bases and applications of an injury severity index for soft tissues." SAE transactions (1986): 672-691.
[3] "Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation - Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures" No. 2009-06. Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), 2009.
Overview
Directive 96/27/EC is a directive adopted by english parliament to ensure motor vehicle saftey duriong side impacts. This directive uses thorax deflection to calculate viscous criterion. This injury criteria is used to predict soft tissue injuries in the soft tissues of the thorax.
Inputs
Signals
- Thorax Deflection (Sternum Deflection, Chest Deflection, or Rib Deflection for Side (Y) Impacts)
Calculation
- Filter the thorax deflection (CFC = 180)
- Differentiate deflection using equidistant differentiation method
- Calculate Viscous Criteria vs Time
- Take the maximum of the Viscous Criteria vs Time
Injury Criteria
Injury criteria for chest from IIHS [2].
| Parameter | IARV | Good - Acceptable | Acceeptable - Marginal | Marginal - Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternum Deflection (mm) | -50 | -50 | -60 | -75 |
| Sternum Deflection Rate (m/s) | -8.2 | -6.6 | -8.2 | -9.8 |
| Viscous Criterion (m/s) | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
References
[1] 96/27/EC "Protection of occupants of motor vehicles in the event of a side impact and amendment of Directive 70/156/EEC". 1996.
[2] "Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation - Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures" No. 2009-06. Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), 2009.
Overview
The NHTSA SID ATD uses a specific combination method similar to the second SAE method.
Inputs
Signals
- Rib Deflection (Y)
- Rib Acceleration (Y)
- Spine Acceleration (Y)
Calculation
- Filter the rib deflection data according to SAE J211-1 (CFC = 600)
- Subtract Sternum Acceleration and Spine Acceleration
- Filter Acceleration Difference (CFC = 600)
- Integrate Acceleration Difference
- Convert to m/s
- Calculate Viscous Criteria vs Time
- Take the maximum of the Viscous Criteria vs Time

Injury Criteria
Injury criteria for chest from IIHS [1],
| Parameter | IARV | Good - Acceptable | Acceeptable - Marginal | Marginal - Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sternum Deflection (mm) | -50 | -50 | -60 | -75 |
| Sternum Deflection Rate (m/s) | -8.2 | -6.6 | -8.2 | -9.8 |
| Viscous Criterion (m/s) | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
References
[1] "Frontal Offset Crashworthiness Evaluation - Guidelines for Rating Injury Measures" No. 2009-06. Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), 2009.